
To provide the house with water, a number of systems are involved. They should be balanced among themselves according to key characteristics. I am not a designer and not an installer — a simple resident. I’m in the middle of exploitation. And to do this, you need to know the principles and features of the operation of all water supply systems of our housing. And, of course, I am interested in how similar systems are arranged in other houses.
Where ‘s the water from
In many suburban settlements there is a water supply, in other cases a well or well is needed. The depth of the well or well depends on the terrain.
The well is usually placed on a plot outside the buildings, although one of my friends has it located right in the house, under the kitchen. Each of these solutions has advantages and disadvantages.
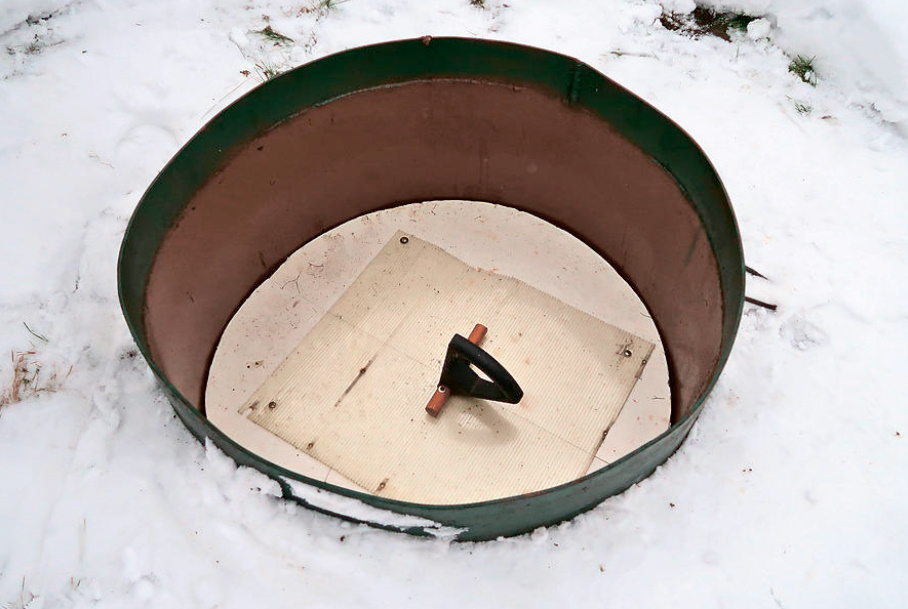
The photos below show the placement of the well on the site in a caisson made of a meter-diameter steel pipe.
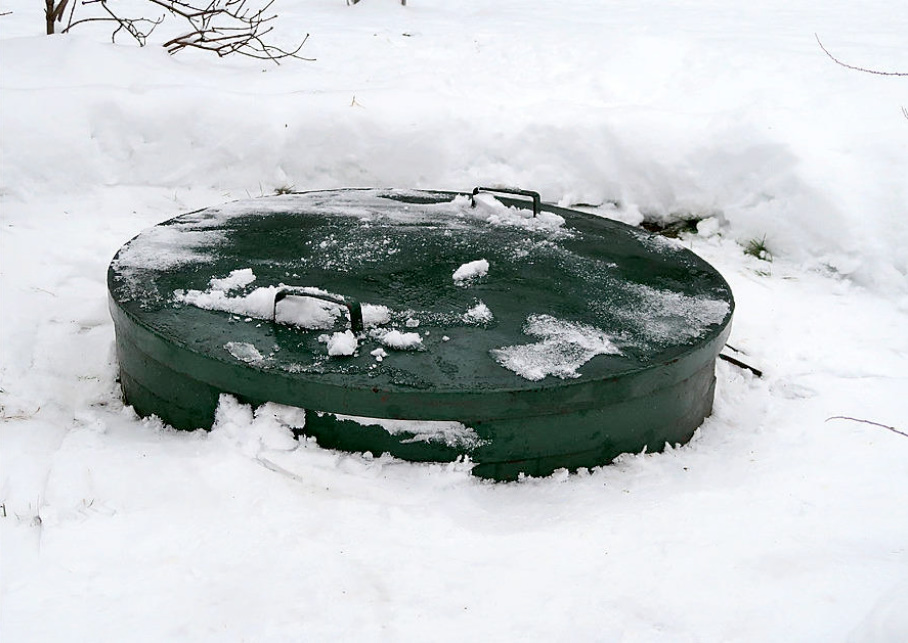

The head of the well is located below the standard depth of soil freezing in this area. The owner has a claim to the device of this caisson — there is no pit in the floor where water would be collected.
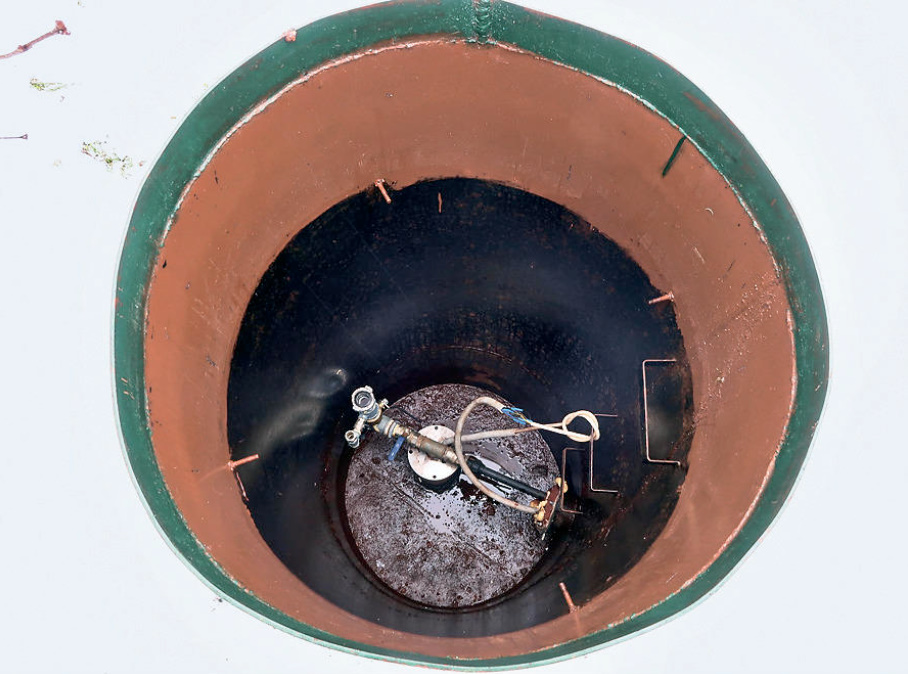

This is both condensate and seeping water from process holes, although they are with seals. A drainage pump can be placed in the pit and the water collected in the caisson can be pumped out.
And this owner uses a conventional pump and a hose with a check valve for pumping.
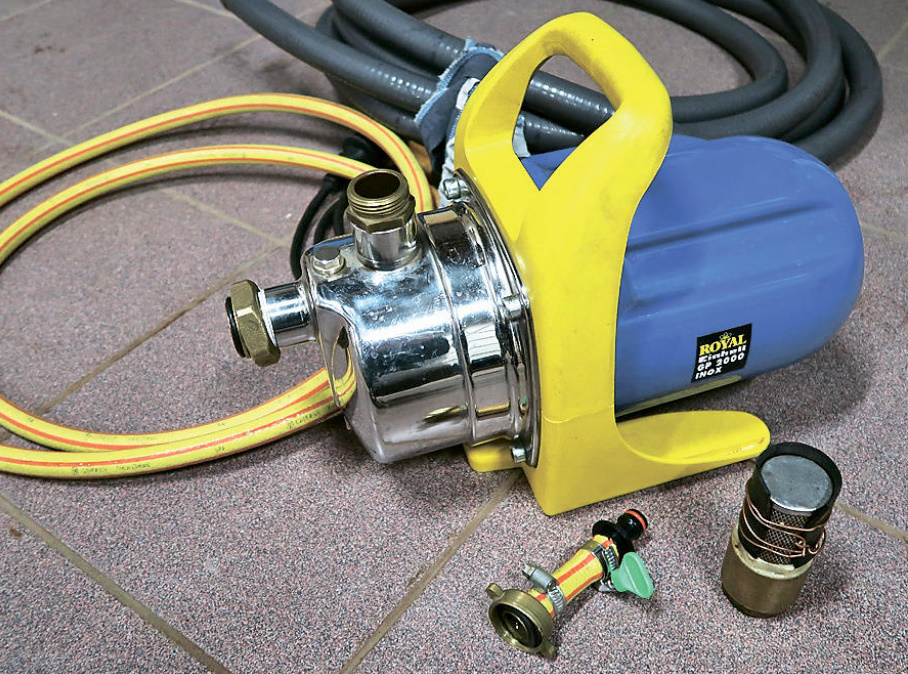

In order to collect almost all the water from the floor of the caisson, a piece of rubber is put on the valve, covering most of its surface.
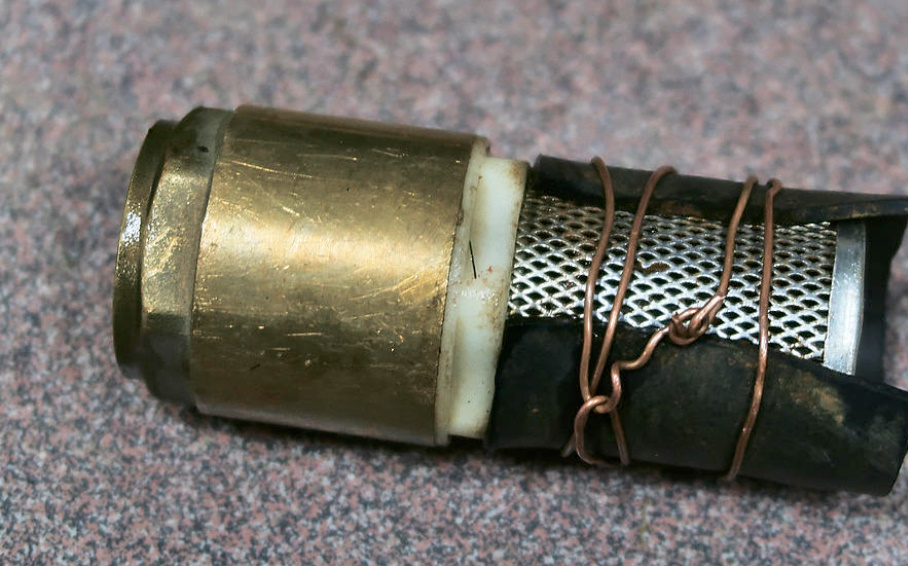

When installing this caisson, it was also not calculated that the ground level next to it would rise slightly after construction due to the addition of a fertile layer for the lawn. I had to weld the strip during operation.
At the outlet of the well there are taps for direct water extraction, including with a connector for a fire hose.
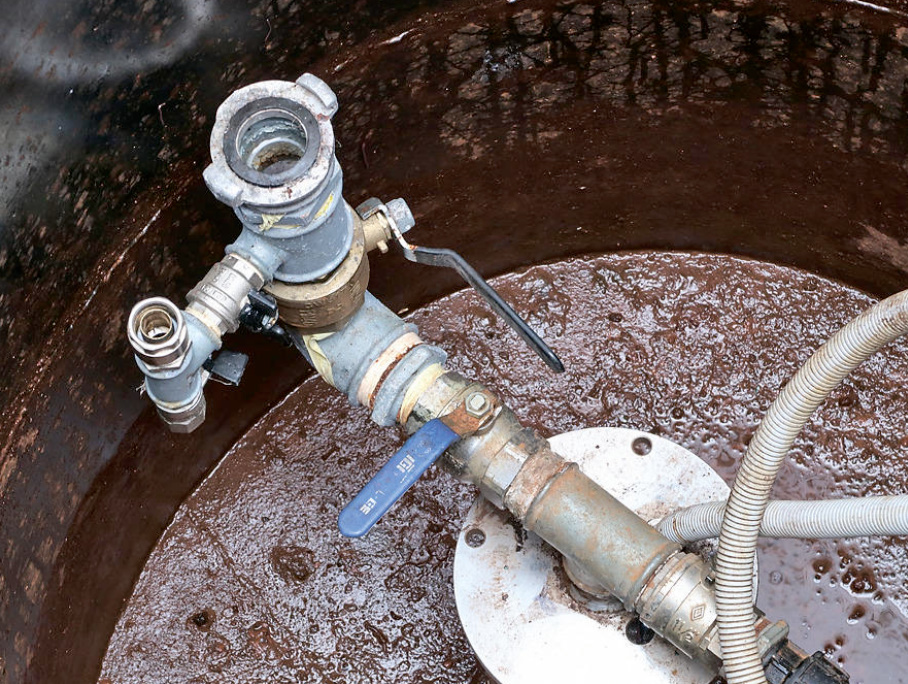

The pipe from the well is also laid below the standard depth of soil freezing. To insulate the caisson, it provides a second cover made of thermal insulation materials.

Pumps for wells are selected according to size — for the diameter of the pipe. The source of electricity is single—phase or three-phase, according to power, depending on the planned volume of consumption and pressure in the system, and according to the method of pressure control in the water supply system.
The suspension of the pump in the well pipe is also an interesting topic, but it will not be discussed here. Also, this article does not address the issues of water intake from a well or connection to external water pipes.
Maintaining water pressure in the system
The water pressure switch can turn on/off the borehole pump. Or, as for example, in the Grudfos SQE family of pumps, the control unit of the pump itself “does” this.
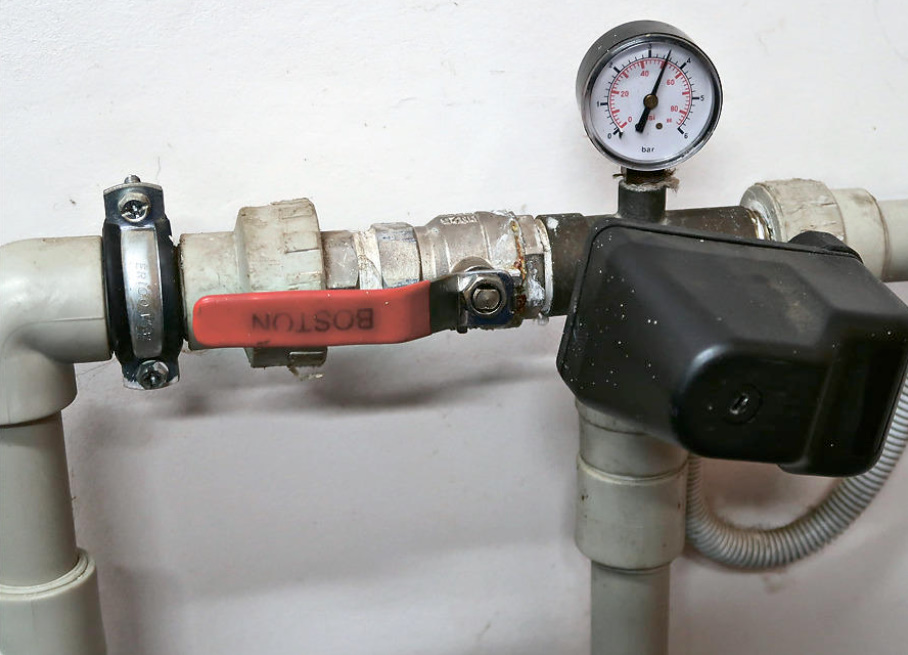

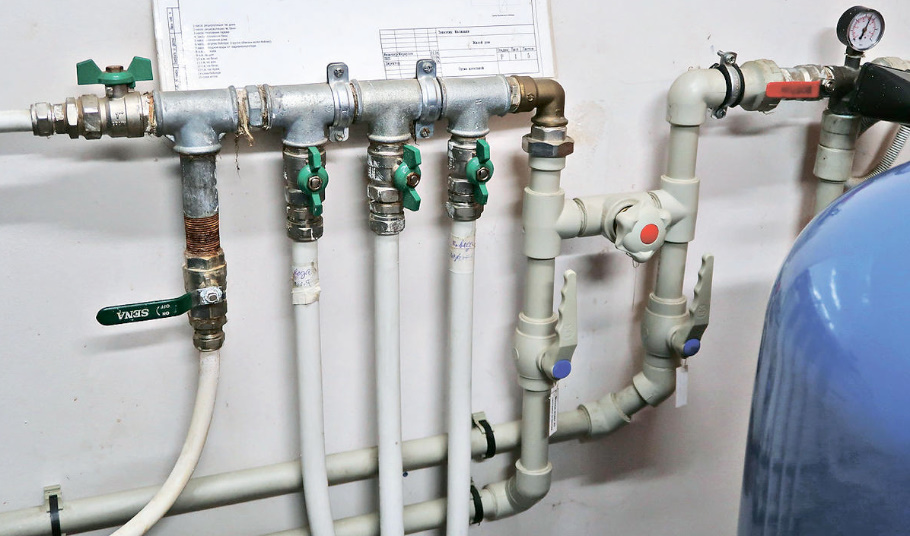
In the first case, a hydraulic accumulator is usually used — a membrane tank — and a fitting with five outlets connecting the pipeline from the water intake, a pressure switch, a pressure gauge, a hydraulic accumulator and a pipeline that supplies water further into the system.
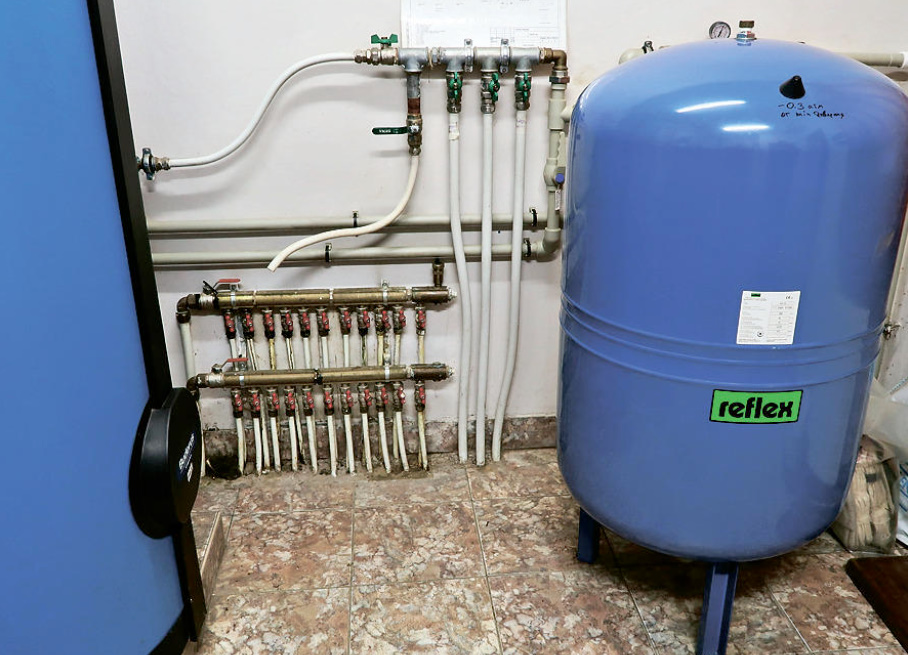

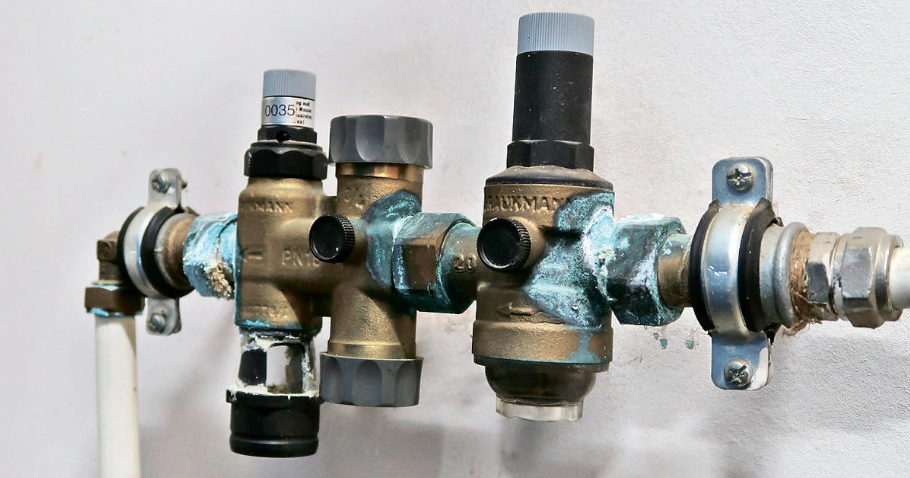
It is often recommended to put a coarse filter on the pipeline from the water intake before the fitting.
The accumulator is needed to maintain a stable pressure in the system, it protects the water pump from premature wear due to frequent switching on, protects the system from possible water shocks when the pump is turned on.
There are different types of accumulators: membrane and with a rubber bag (both the membrane and the bag are hidden inside the accumulator); vertical and horizontal. For cold water — usually blue, expansion tanks for heating systems — red. The rubber in them is different, at least it should be! There are models made of stainless steel. The size of the tank depends on the maximum estimated volume of water consumption per unit of time.
The minimum and maximum water pressure in the accumulator is set on the pressure switch. The description of the method of selecting their values is quite voluminous and will not be considered here.
Over time, you will notice that the water pump starts to turn on more and more often. Therefore, with year-round operation 2-3 times a year, it is recommended:
- Disconnect the pump from the power supply;
- Drain the tank completely;
- Re-pump air into an empty tank.
Before this procedure, with the system still running, note the minimum pressure when the water pump is turned on. After draining the water, pump the air 0.3 atmospheres less than this marked value.
To pump air on tanks with a volume of 100 liters or more, there is a hole with a nipple and a thread, like on car tires. In the photo below, it is covered with a plastic plug.

The air pressure gauge when pumping should be used with a scale of high accuracy. Water pressure reducers are also used to stabilize the water pressure in the system and limit its critical level.

Water purification
The first stage of water purification is its mechanical purification from large particles. Whether additional cleaning is needed can only be shown by a chemical analysis of the water.
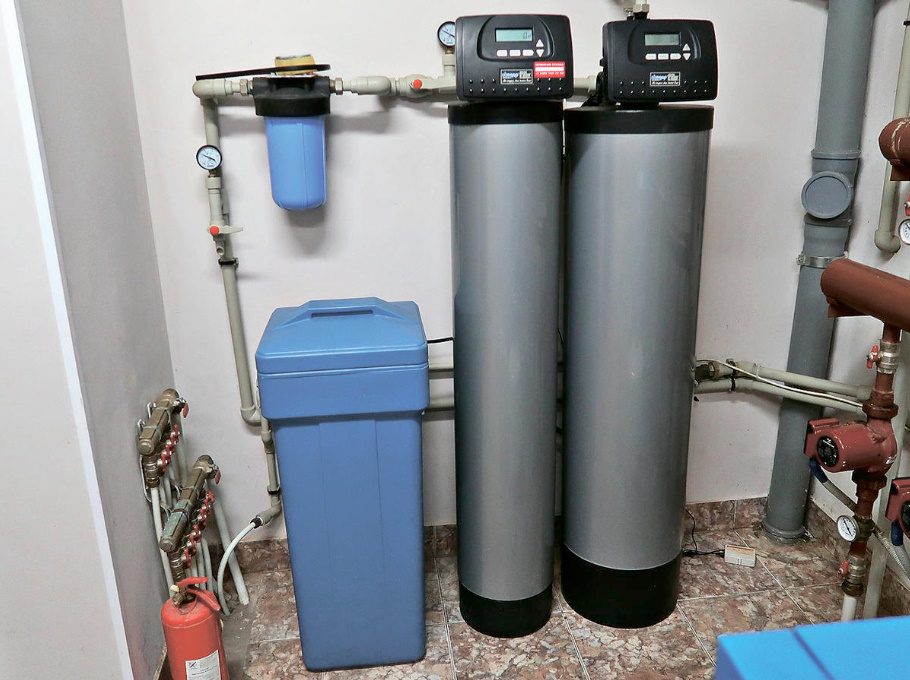

The photo above shows an installation consisting of a salt tank, a fine filter, a softener column, a degreaser column, a coarse filter and an Aquastop system.

The hose for flushing the coarse filter (mud) is removed to the sewer.
According to the results of the chemical analysis , they were not needed: a) aeration cleaning to remove hydrogen sulfide and other gases dissolved in water, b) an ultraviolet lamp for disinfection.
The cleaning system was installed in the boiler room a few years after the construction and installation of equipment in it. It was necessary to mount the pipes of the bypass of the treatment system and the taps of its shutdown — the photo below shows the place of insertion into the pipe after the hydraulic tank.

And also the cleaning system had to be bypassed to supply water for watering the garden, lawn, etc. When designing such a system, its characteristics should be linked to the septic tank device — a single flush requires several hundred liters of water!
Filters of the same system “eat up” the water pressure — you have to raise it before the treatment plant. And, of course, maintenance is required — 3-4 times a year.
Interestingly, I saw some neighbors’ water treatment columns wrapped in polyethylene foam foil cloth. It turned out that this is how they struggle with the appearance of condensation on their surfaces.
Hot water
Water heating can be carried out by water heaters: flow—through or storage – boilers.
For the boiler, the accumulator is used as an expansion tank. Heating up, the water expands, increasing the volume in the water supply system, and since it does not have the property of contracting, the minimum volume increase in a confined space increases the pressure and can lead to the destruction of the system.
The photo below (on the left) shows the white hydro tank used in the hot water preparation system.
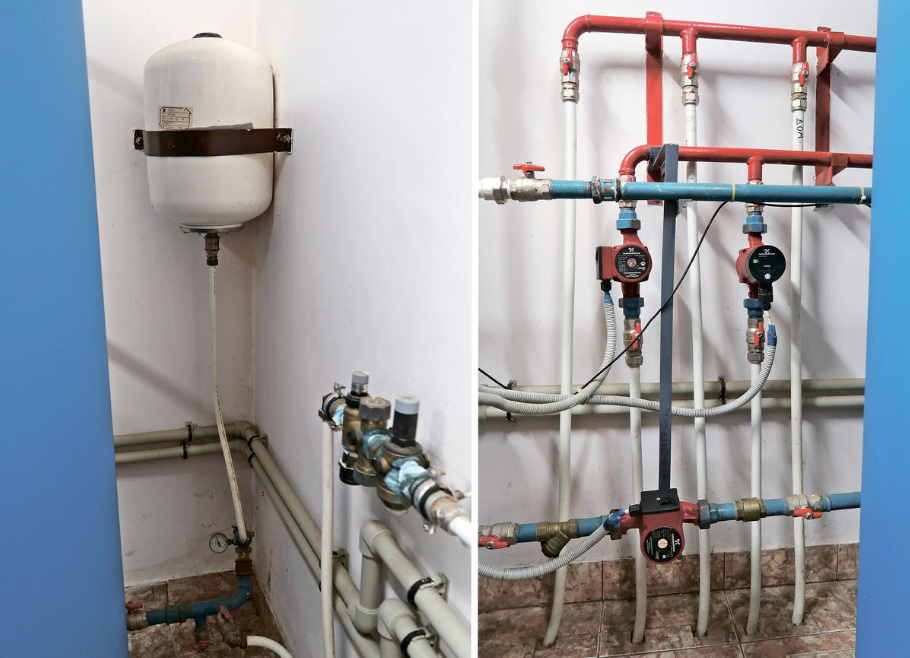

The volume of hot water consumption for the house requires the choice of the layout of the boiler with a heating boiler: built-in or external. If the supply of cold water to the taps in kitchens, toilets and showers is carried out due to the water pressure existing in the pipes, then a constant or periodic circulation is usually organized for hot water. Yes, otherwise you will not heat the pipes of heated towel rails.
Such circulation is controlled by the “brains” of gas or electric boilers. This requires electric circulation pumps. In the photo above (on the right), two upper pumps circulate hot water in two different buildings, and the lower one exchanges hot water between the gas boiler and the external boiler.
Boilers also control the temperature of hot water. At the same time, the choice of the minimum temperature value by the host affects the microflora of water in the system. I chose +55°C for myself. And again, we should not forget about routine maintenance of installed systems. For example, replacing or cleaning magnesium anodes in boilers.
Wiring by consumers and… the project!
Pipes, taps, fittings, combs and so on, so on, so on.
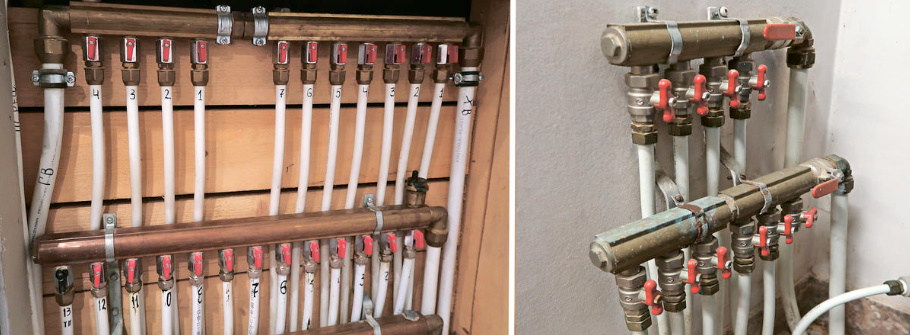
As you can see, water supply is connected with heating, power supply, security, fire fighting, septic tank and landscape organization. From all of the above, I think it becomes clear that the systems mentioned here need a systematic approach. That is, the project. And before the project — the terms of reference: how many people will live, what is their lifestyle, etc. And after the work is completed — the executive documentation (“text and graphic materials reflecting the actual execution of design decisions and the actual location of objects …”), equipment operating instructions. And information about what others have, what they have come up with new, how they live and use all this equipment.




Leave a Reply