It happened to you: you come at the beginning of the season for the first time to the country — all in plans, seedlings, joyful anticipation — and you see that during the winter on the site there were irreversible changes for the worse… the Fence fell down, the tile sheet on the roof came off, the greenhouse was pressed by snow, the path “swam away”. And hands fall, the mood deteriorates, and forgotten in the hassle of restoring the garden seedlings dry near the barn.
It’s a shame, annoying, but what to do — is to roll up his sleeves and get down to business. And in order that in the following spring the feeling of a holiday from the beginning of a country season was not overshadowed by a type of breakages and losses, it is necessary to repair correctly. Consider what spring incidents happen to garden paths and how to avoid them.
What are the tracks
As part of the question about the options for damage and, accordingly, the ways to repair the tracks, are not interesting varieties of coating materials, and ways to device tracks. And then there is not much diversity — there are only six ways:
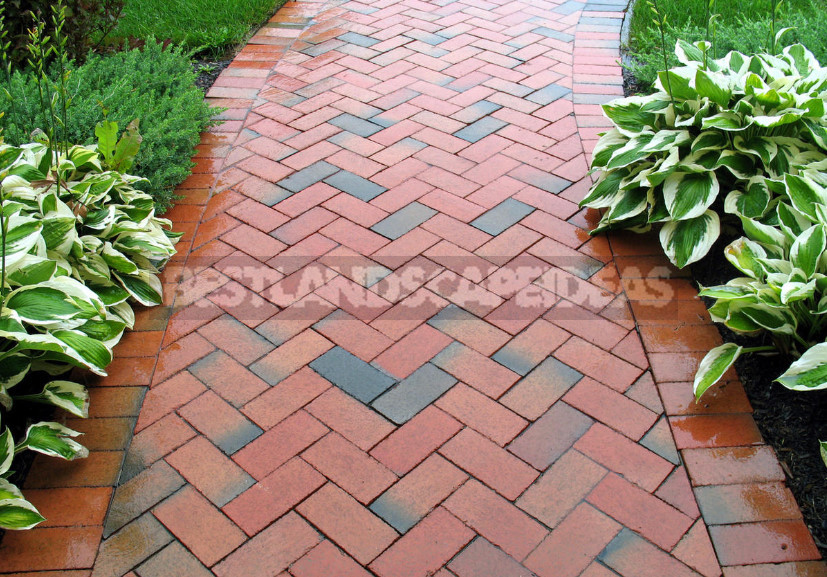
1. Paths with a hard surface — concrete, asphalt, composite materials, self-leveling rubber crumb.
2. Track teams of piece material on a soft base — paving of paving stones, clinker, stone slabs, boulders, large-format concrete slabs, wooden bars and more.
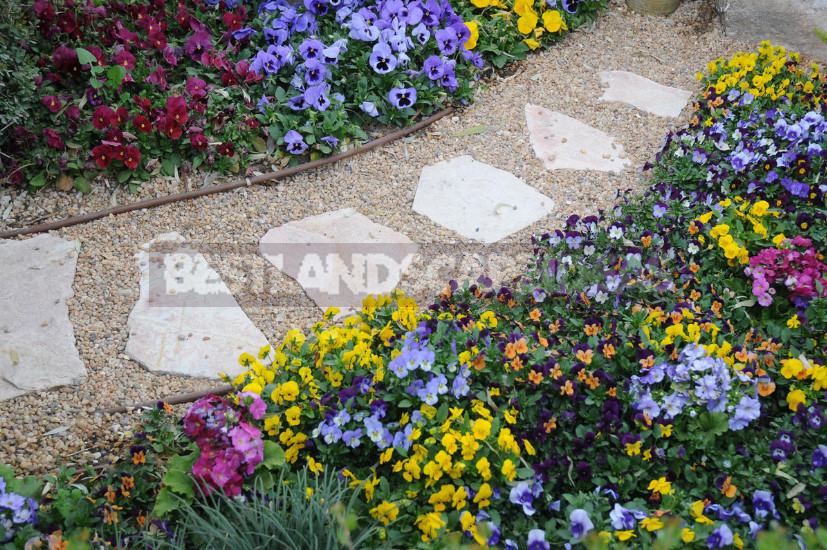

3. Soft paths — gravel, sand or any other loose compacted material.
4. Tracks of rolled materials — covering for the street, similar to linoleum.
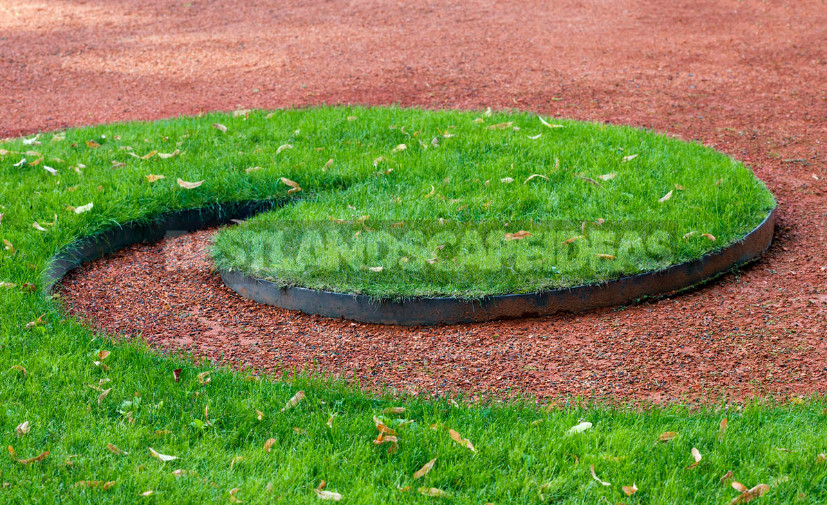

5. Ground or lawn paths — with grass covering, resistant to trampling.
6. Walkways-walkways — wooden structures, raised on small supports.

There are also paths that are formed in areas of the most intense movement of people — as a rule, they have no reason. And combined tracks that combine, for example, paving elements and lawn or coating of different bulk materials.
Problems after winter with garden paths happen, in General, for one reason — they were incorrectly made. Or the owner of the suburban area did not take into account the peculiarities of his site and chose the wrong type of track.
What happens to improperly arranged tracks
The main trouble that can happen to the garden highway — the destruction of the underlying layer. Usually this happens for reasons independent of us: as a result of deformation of the soil, leaching of sand, digging animal holes, spreading the roots of trees. But in some cases, the owner himself is to blame, who did not bother to make a quality Foundation for the track.

If the base of the track is made of insufficient thickness or poorly compacted, expect sagging plates and pavers, cracks on the concrete surface, the formation of trampled ruts and pits on gravel paths.
The same phenomena can be observed by the summer resident and as a result of the action of the frosty heaving peculiar to clay sites. In autumn the clay is soaked with water and swells, and in winter the water freezes and increases in volume, destroying the track. And the coating of concrete can collapse if it does not provide transverse damper seams, which make in order to compensate for the geometric deformation of the track.

After the winter, the top layer of the concrete path can collapse if the technology was broken during its construction — for example, the solution was poured in layers. Or if the concrete layer was too thin.
Many gardeners make the same mistake: put the tiles on the street on a normal tile adhesive. Although for outdoor work it is necessary to use a special glue that can withstand the freezing-thawing cycle. Therefore, the destruction of tiled garden paths occurs quite often.

The main thing is that inside
Different types of paths require different preparations. But there are General rules that are suitable for any options. Garden paths — “this is not just so”: this is the most that neither is the construction. And like any structure, they require a solid Foundation. The basis of the track — the underlying layer of compacted sand and gravel cushion.
The thickness of the underlying layer depends on:
- coating material;
- load on the track — the pedestrian path is different from the site on which the car drives. The path on which I go most often needs to have a more solid Foundation than that which is used from time to time;
- from the properties of the soil and groundwater level.
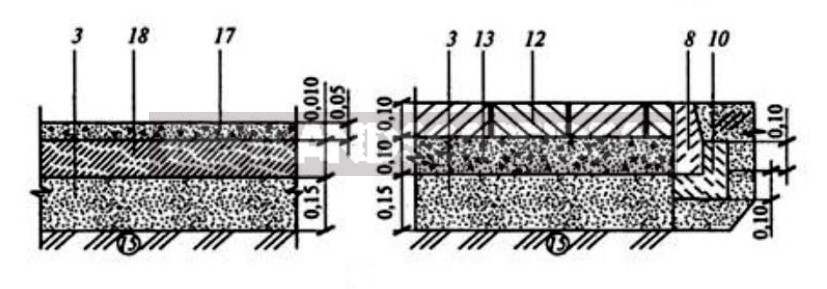
3 — sand; 8 — garden side stone; 10 — concrete; 12 — concrete paving slabs; 13 — dry cement-sand mixture; 18 — limestone rubble; 17 — special mix (granite sowing — 60%, sand — 10%, clay — 20%, lime — 10%).
Track slope and drainage
So that rain water does not accumulate, it is necessary to arrange the bias of the fabric of the track. If it is wide, it is advisable to make a uniform slope from the center to the edges. To make a narrow tilt to one side.
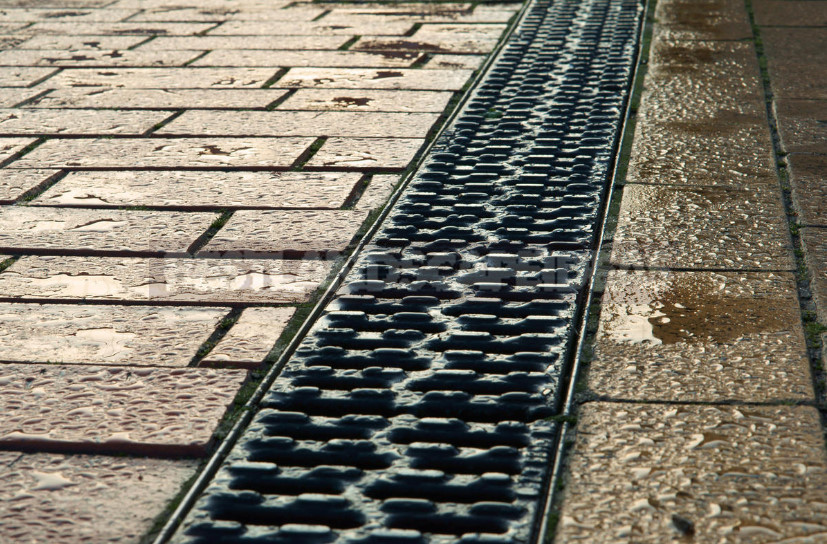

It will not be superfluous and drainage device under the track or next to it. And if after the rain on your site there are puddles, it does not interfere to think about the drainage system of the entire site.
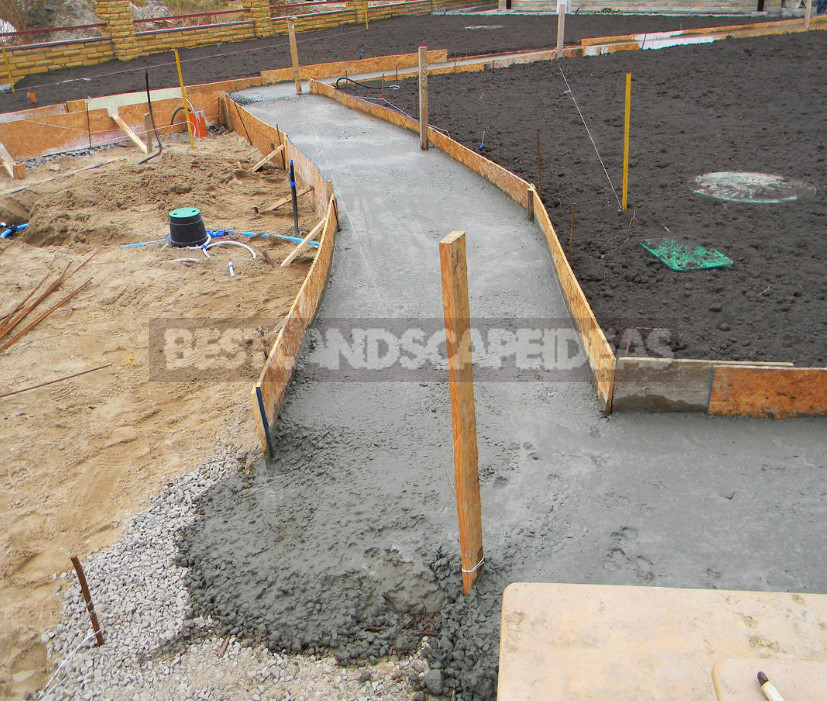
The correct device paths
For the device of the track, the soil is excavated to a depth of at least 300 mm — the fertile layer is removed to a dense base. Then the geotextile is laid in the form of a trough. The geotextile laid on the sand with Strait water and tamper. In the finished (compacted) form, a layer of sand should be about 150 mm. on Top of the sand — another layer of geotextile and on top of it — crushed stone, also compacted.

The gravel-sand cushion breaks the capillarity of the soil, distributes the load and prevents deformation of the soil under the track from frost heaving. The purpose of geotextiles — stabilization and reinforcement of the underlying layer. The first (lower) layer of geotextiles prevents the washing of sand into the soil, and the second — does not allow gravel to mix with sand. In addition, geotextile improves soil drainage under the track, prevents weeds from sprouting through the coating and reduces the destructive activity of animals.

After creating the underlying layer, you can proceed to the covering. If you plan a concrete or asphalt track — you need to install the formwork and pour the solution. For paving — lay another layer of geotextiles, lay a layer of cement-sand mixture and start laying stones or slabs. For a green track to make a lawn using a geogrid.

If you find in the spring “dancing” or swollen tiles, cracked concrete floor or just puddles and pits on the paths in the garden, do not try to engage in “patching”. Patching holes and covering the cracks will not solve the problem — next year you will see the pits and cracks again. Approach to work reasonably from the very beginning, and then you do not have to deal with regular spring repair of garden paths.







