
The chemical industry works well with us, it supplies the gardener with various mineral fertilizers. And even with excess! Take, for example, tuks containing one of the main nutrients for plants — nitrogen. When you come to the garden store, your eyes run away: there is an azofoska, there are a variety of saltpeters and a bunch of varieties. A fertilizer with a funny name urea stands apart.
That’s how we’ll start to figure out what the differences and advantages are, as well as when and how much to make it.
What is urea
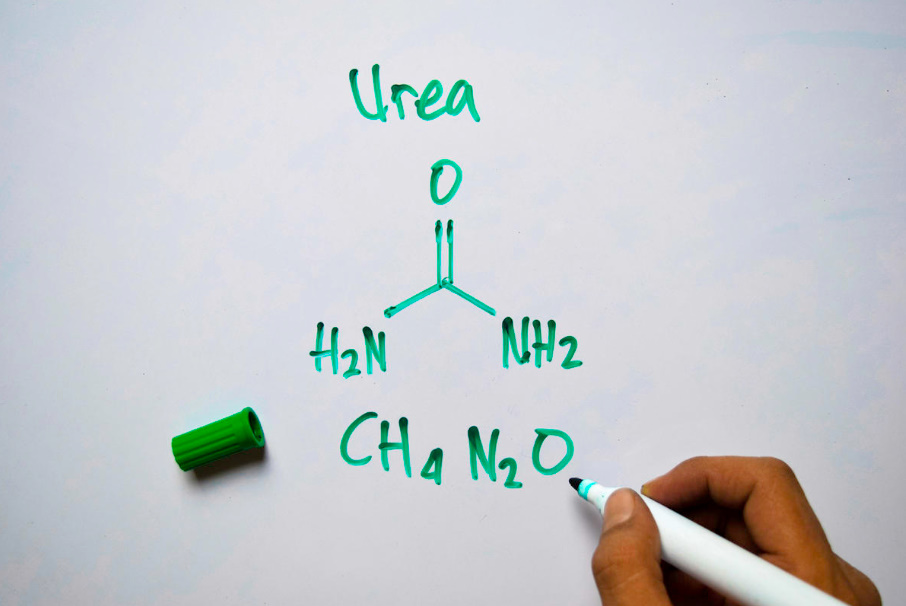
Urea is a natural compound, the end product of protein transformation during metabolic processes in mammals and in some fish. By its concentration in the blood serum, a biochemical analysis is carried out to assess the work of internal organs, and by the amount of urea released in the urine, doctors judge the need for protein. This compound was discovered for the first time in urine, which is why it received this name. Another name of the substance — carbamide — indicates its chemical essence. Urea (CH₄n₂O) is a derivative (diamide) of carbonic acid.
Carbamide (or urea) is the first organic compound artificially synthesized from inorganic substances. Now it is industrially produced from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
Urea is quite widely used:
- in industry — for the production of fiberboard, chipboard (for the manufacture of modern furniture) and similar materials;
- as a reagent for diesel engines — cleans exhausts to acceptable standards (according to European standards);
- for cleaning flue gases of boiler houses, etc.;
- in animal husbandry — as a feed additive.
Urea is also needed in cosmetology: it is used in products for the care of fading skin. The food additive E927b is also urea, used as a glazing agent, anti—foaming agent, normalizer of acidity. And yes, there is urea in the gum, too.
Urea as fertilizer
Urea is best known to summer residents as one of the most common nitrogen-containing fertilizers. The main consumer of industrially synthesized urea is crop production, for which more than 100 million tons are produced annually in the world.

Urea belongs to the group of amide nitrogen fertilizers, that is, the nitrogen in this fertilizer is in organic form — in the form of carbamic acid amide (nh₂-). Urea is the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer (46.2% nitrogen in it) and the most economical. Two varieties are produced — brands A and B. The first is for animal husbandry and industry, the second is for crop production.
Urea grade B is colorless or white granules or crystals that dissolve well in water. During production, acidifiers are added, so urea is perfectly stored, does not clump, and dissipates well during machine application. However, this substance is very hygroscopic, so it should be kept in a place protected from moisture.

When and how much to deposit
Urea can be used to fertilize any crops and in a variety of cases:
- as the main fertilizer,
- for early spring fertilizing of perennial crops,
- for root and non-root fertilizing during the growing season,
- in irrigation systems for fertigation and hydroponics.

The application rates of carbamide depend on the culture, but in general, from 1.3 to 2 kg, that is, about 20 g per 1 m², is applied to 100 m² as the main fertilizer in autumn for vegetables, flowers and berry planting. For spring feeding of vegetables and flowers, before sowing — 0.3-0.4 kg, for berry crops — 0.4-0.7 kg (3.5-5.5 g/m²).
For liquid root fertilizing, 30-65 g of urea is diluted in 10 liters of water — the solution is enough for processing 10 m². For fertilizing the leaves, 50-100 g of urea is dissolved in 10 liters of water. This amount will be enough to spray approximately 150 m² of plantings. The urea solution in the correct concentration is not toxic to plants, the leaves do not get burned when sprayed.
Fertilizer Features
Such a variety of fertilizers containing the same element of nutrition is offered by manufacturers not because chemists know a lot of different substances, compounds, and they can portray all this in the form of all sorts of chemical formulas. The efficiency, cost-effectiveness and digestibility of fertilizer by plants depend on the form of nitrogen. In addition, when choosing nitrogen-containing top dressing, you need to focus on the type of soil, ambient temperature and soil moisture.

Since urea is easily soluble, when it gets into moist soil, it turns into a soil solution. Then, within 2-3 days, under the action of urobacteria (capable of decomposing urea with the help of the urease enzyme), the process of ammonification occurs — ammonium carbonate (ammonium carbonate, (nh₄)₂co₃) is formed. Hence follows one of the disadvantages of urea — fertilizer does not work in cold soil. The greatest effect is achieved when the soil is heated to +15 ° C. Therefore, for spring feeding of early-awakening perennial crops (for example, currants or gooseberries), as well as winter plantings of garlic and onions, it is worth choosing another fertilizer containing nitrogen.
There is another feature of urea. Studies have found that plants can partially consume urea that has not been ammonified: in addition to urobacteria, urease is produced by green organisms themselves. That is why urea is considered the best nitrogen fertilizer for fertilizing leaves: the substance can be absorbed by the whole molecule without requiring preliminary decomposition. A positive feature of the fertilizer is a quick effect: already on the second day after foliar fertilization, the amount of nitrogen in plant proteins increases.
Being an unstable compound, upon contact with air, ammonium carbonate decomposes with the release of ammonia gas (nh₃). Therefore, in order to avoid its evaporation when applying carbamide, it is necessary to seal the fertilizer into the soil. Nitrogen losses from uncultivated fertilizer increase in the absence of precipitation and on soils with neutral and alkaline reactions. For fertilizing during the growing season, it is more convenient to use urea solutions.

If the carbamide is safely hidden in the soil, another reaction occurs with ammonium carbonate — as a result of hydrolysis, ammonium hydroxide and ammonium bicarbonate are formed. The resulting ammonium is gradually absorbed by plants.
Everything is according to the rules
To get the desired result, it is necessary to apply urea in the garden and vegetable garden, taking into account some restrictions.
- Urea is a spring fertilizer. When applied in autumn, most of the nitrogen will go into deeper layers of the soil and become inaccessible to plants. The exception is sandy and sandy loam soils.

- Top Dressing with urea is not recommended during budding: plants may begin to fatten, shed some of the buds or postpone fruit formation and maturation.
- It is not necessary to use urea simultaneously with ash and lime fertilizers, as a chemical reaction begins, increasing nitrogen losses. It is also better to time the introduction of carbamide and superphosphate in order to prevent the formation of compounds with phosphorus inaccessible to plants. If, after all, the introduction of phosphorus is necessary, use phosphorous flour.

- It is useful to apply urea together with organic fertilizers, reducing the dose taking into account the content of nutrients in organic matter.
And what else?
Urea for crop production is not only a fertilizer, but also a means of combating pests and diseases. Potato nematode, Colorado potato beetle, weevil, aphid — concentrated (500 g per 10 liters or even 1:1) solution. Also, a solution of carbamide will help fight the scab of pears and apples.

Carbamide is an effective and useful tool for the vegetable garden and garden, with skillful use, it supports and protects the crop. Do you use urea on your site?




Leave a Reply