In winter, this device allows you to save on heating, and in summer-on cooling. In addition, thanks to the recuperator, it is possible to organize a full-fledged ventilation and heating system, creating additional comfort for living in the house.
How it works
Heat recovery is a heat exchange process in which the cold air entering the room is heated by the heat being removed. Similarly, cooling recuperation takes place: the cold of the air being brought out is transmitted to the warm supply air masses.
For the organization of heat/cold transfer, special devices – recuperators are used. In fact, these are heat exchangers through which the supply and exhaust air flows pass without mixing with each other.
Some models are equipped with a low-power electric heater, which automatically turns on if the difference between the indoor and outdoor temperature is too large. Modern devices are also often equipped with filters, humidifiers, ionizers, a noise suppression system and other useful devices.
Advantages and disadvantages
Thanks to recuperation, the amount of heat energy required for heating housing is reduced. Accordingly, the cost of its production is reduced. You can also save money on the operation of the air conditioner in the summer. However, before recuperation-based ventilation starts to work and pay off – it will require certain investments, which can be very significant.
Types of recuperators
For recuperation in the supply and exhaust system, several types of units are produced
Lamellar
The design of this type implies the presence in the heat exchanger of special plates of a wave-like configuration, which are made of sheet material that conducts heat well (aluminum, steel, plastic).
Plates in the amount of 60-70 pcs. are mounted in a single unit (radiator) in such a way that the channels formed by the “wave” do not run parallel, but cross each other. Due to this, air masses with different temperatures do not mix with each other.
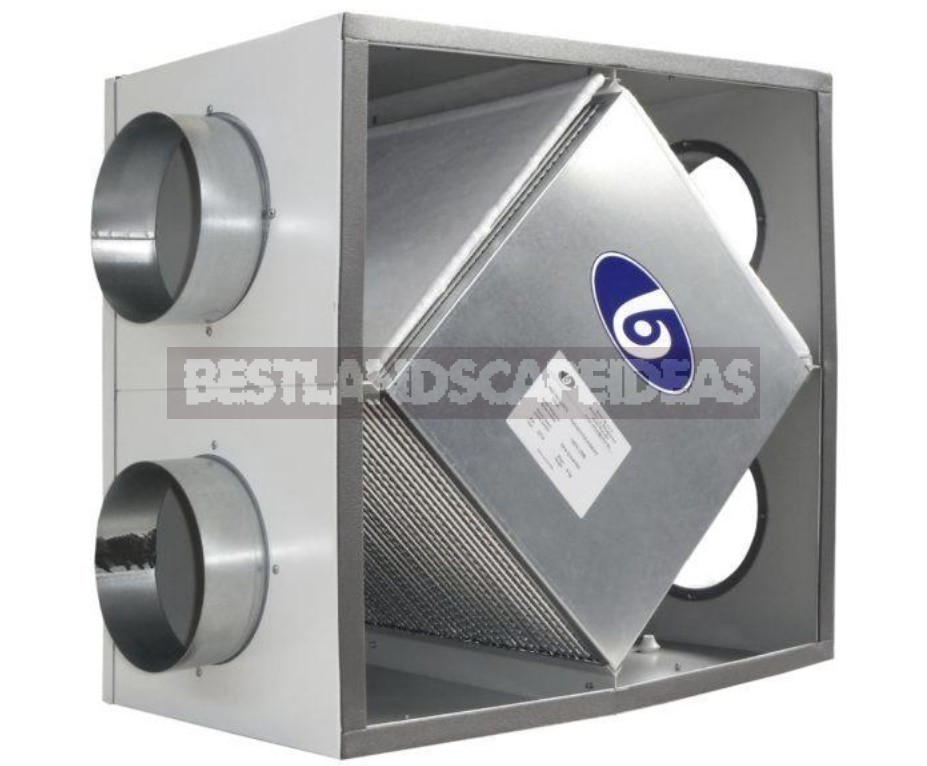

The main drawback is the risk of freezing, which occurs due to the fact that moisture settles on the walls of the mechanism, which is carried by a warm stream. To prevent the condensate from turning into ice, the cold supply air must periodically be allowed directly – i.e., bypassing the recuperator.
Rotary
In this modification, the heat exchanger is a rotor-a rotating cylinder made of corrugated steel. After heating up from the exhaust air, the rotor is rotated in half a turn and immediately transfers heat to the supply flow. And then – in a circle.
The advantage of the device is that it is not exposed to the risk of freezing, since the speed of rotation of the cylinder is adjusted automatically, so that it does not have time to accumulate moisture. This unit does not need to be “defrosted”, so its efficiency can reach up to 95%
Liquid
It consists of two heat exchangers connected to each other by a pipeline with a liquid coolant circulating in it. As the latter, a solution of propylene glycol with distilled water is usually used.
When heated in the heat exchanger in the exhaust duct, the liquid transfers heat to the incoming air through the heat exchanger in the supply duct. The device does not freeze and is able to serve large rooms. It is rarely used in residential buildings.
How to choose a heat exchanger?
The best option is to initially design a ventilation system with a built-in heat exchanger. In this case, we are talking about the purchase of a supply and exhaust system, the design of which already includes a heat exchanger.
The main selection criterion is the performance of the entire system as a whole (m³ * h). It is calculated based on the total volume of air in the room. To calculate it, you need to multiply the area of the house by the height of the ceilings (V = S*H). To the result obtained, experts recommend adding 20%. This will help to take into account the resistance with which the air flows will meet, passing through the various grilles and filters of the system.
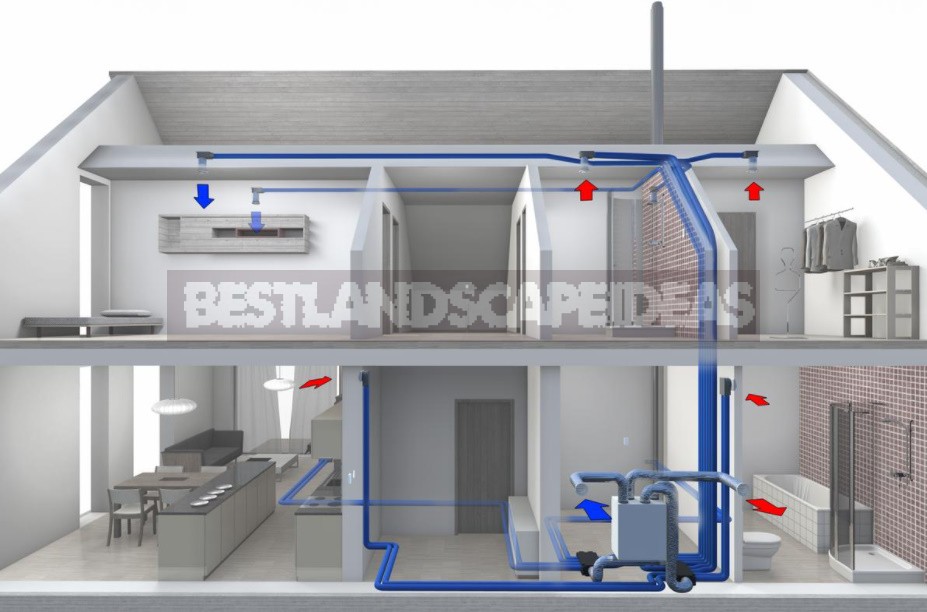
Sometimes the decision to purchase a heat exchanger occurs after the ventilation is fully installed. As a result, there is a task to choose a device for a ready-made and functioning air exchange system.
When choosing, you should focus on the total volume of supply air that passes through all the fans to the heat exchanger. The performance of the unit must be 25% less than this value, otherwise it will not fully work and may be useless.
In addition, it is necessary to pay attention to the holes for connecting the air ducts. It is desirable that the dimensions and configuration of these openings are the same as those of the air channels in the ventilation system. Otherwise, there may be problems with the installation of the device.
Calculation of recuperator efficiency
How well the heat exchange device copes with its task can be understood by such an indicator as the recovery efficiency coefficient. This value is the ratio between the maximum possible amount of heat that can be transferred to the supply air and the amount that is actually received. The maximum possible amount of heat means the temperature of the air in the room.
Depending on the device, the coefficient ranges from 30 to 95%. It can be calculated using the formula: Kt = (T3 – T1) / (T2-T1), where
- Kt – the efficiency coefficient of the device in terms of temperature;
- T1 – outdoor air temperature;
- T2 – indoor air temperature;
- T3 – the temperature of the incoming air after passing the heat exchanger.
Let’s assume that:T1 = 3° C; T2 = 20° C; T3 = 12° C As a result: Kt = (12 – 3) / (20-3) = 0,5
Thus, the efficiency of the unit will be: 0.5*100% = 50%
Is it always needed?
In the example shown above, the savings are due to the fact that to maintain a comfortable microclimate in the house, the air must be warmed up by only 8° C, and not by all 23. However, this case is hypothetical. In fact, with such a temperature difference, it is impractical to install a heat exchanger: the reduction in heating costs in such a situation is too insignificant and will not pay off the cost of equipment.
It makes sense to mount the recuperator with its inclusion in the forced air exchange scheme under the following conditions:
- The area of the building is at least 80 m², so the volume of updated air is quite large. For houses with an area of 200-500 m², it is very difficult to do without recuperation;
- The climate of the region where you live is characterized by severe winters with frosts up to minus 20-30° C and stifling summers with heat up to 30-35°C
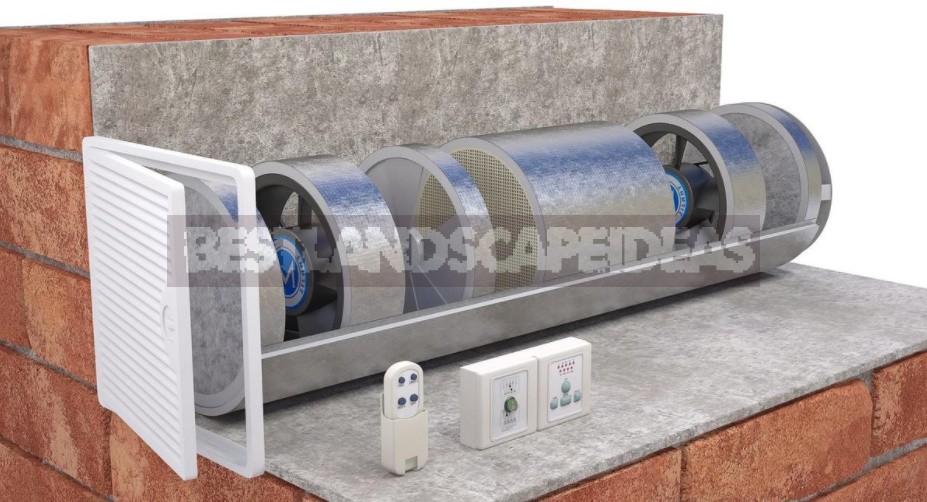

If we are talking about small buildings with a size of 30-50 m², then compact-class recuperators are produced for them. These are mini-systems with supply and exhaust ventilation, heat exchanger, filter and electric heater.
Such devices are most often built into a through hole in the wall. Buy such devices not in order to save on energy, but to create a minimum air exchange and dust filtration.


















